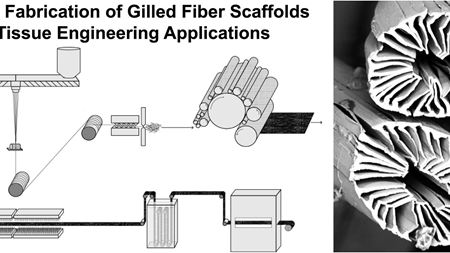
Polymer fibers with ‘gills’ that resemble the underside of a mushroom could improve tissue engineering approaches to bone repair.
31 March 2016Cordelia Sealy
Cambridge researchers have shown that particle size isn’t the only concern when it comes to the risks posed by volcanic ashes.
29 March 2016Laurie Winkless