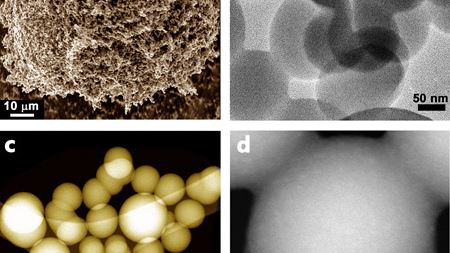
carbon spheres, which can be produced easily and greenly, could adsorb carbon dioxide from industrial processes
29 January 2021Cordelia Sealy
A new model has revealed that the strength of carbon nanotube fibers depends on the length of the nanotubes and the friction between them.
28 January 2021