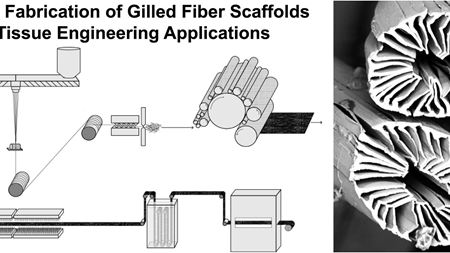
Polymer fibers with ‘gills’ that resemble the underside of a mushroom could improve tissue engineering approaches to bone repair.
31 March 2016Cordelia Sealy
Taiwanese researchers suggest that graphene’s high thermal conductivity could further improve the lifetime of LEDs.
28 March 2016Laurie Winkless